Chronic Pain
The term Myofascial pain describes pain attributed to muscles and surrounding connective tissue. Such pain can be localized or widespread. The most common areas to be affected are neck, shoulders, lower back. Myofascial pain can also affect limbs and scalp. Such pain is characterized by presence of trigger points, located in skeletal muscles. They are areas of hyperirritable muscle tissue, spasming easily, or persistently spasming. On exam these points are very tender and often have palpable knots.
Typical causes of such pain are overuse and injury.
The primary concern with this condition is development of chronic pain. The pain and inflammation create a vicious “positive feedback” cycle, where inflammation within the muscle creates pain, and pain, in turn, causes more inflammation. Eventually the affected area spreads. Myofascial pain can progress into a chronic debilitating pain condition if left untreated. Myofascial pain is a frequent cause of headaches.
TREATMENT
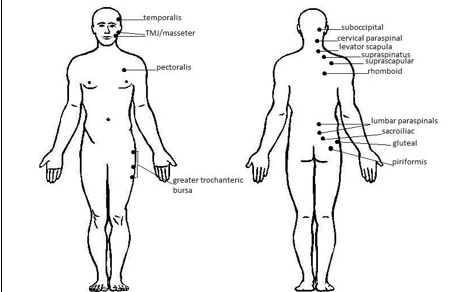
Trigger point injections (TPI) and superficial nerve blocks. On the exam triggers are identified and a medicinal solution is injected into a muscle. This treatment can provide a prolonged symptomatic relief in case of chronic pain. In case of acute pain, series of TPI can stop progression and speed up resolution or recovery from an injury. TPI often performed in conjunction with antiinflammatory medications and physical therapy. Here are some of more common pain sites.
Typical causes of such pain are overuse and injury.
The primary concern with this condition is development of chronic pain. The pain and inflammation create a vicious “positive feedback” cycle, where inflammation within the muscle creates pain, and pain, in turn, causes more inflammation. Eventually the affected area spreads. Myofascial pain can progress into a chronic debilitating pain condition if left untreated. Myofascial pain is a frequent cause of headaches.
TREATMENT
Trigger point injections (TPI) and superficial nerve blocks. On the exam triggers are identified and a medicinal solution is injected into a muscle. This treatment can provide a prolonged symptomatic relief in case of chronic pain. In case of acute pain, series of TPI can stop progression and speed up resolution or recovery from an injury. TPI often performed in conjunction with antiinflammatory medications and physical therapy. Here are some of more common pain sites.